Digeorge Syndrome Ultrasound Findings
Digeorge syndrome ultrasound findings. This syndrome is usually sporadic but can be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion from an affected parent. A 35-year-old healthy primigravida was hospitalized due to preterm labor at 29 weeks and four days. This is where a small piece of genetic material is missing from a persons DNA.
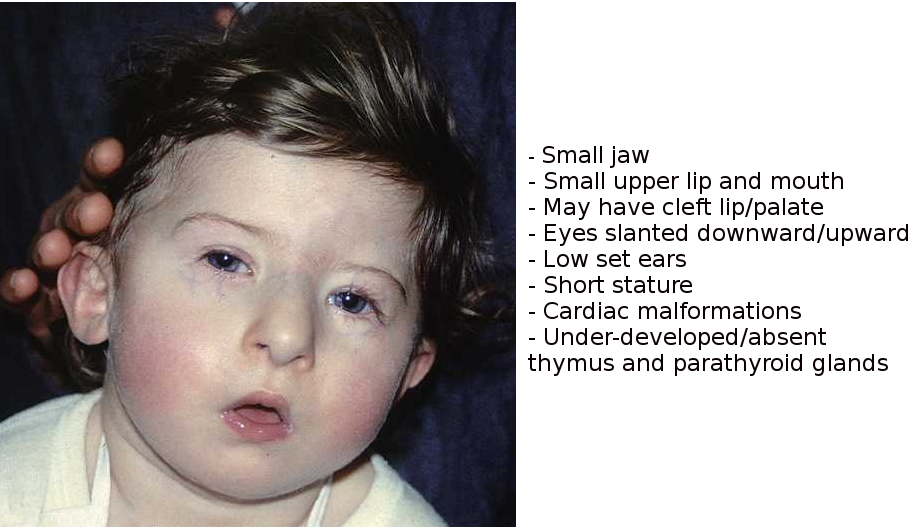
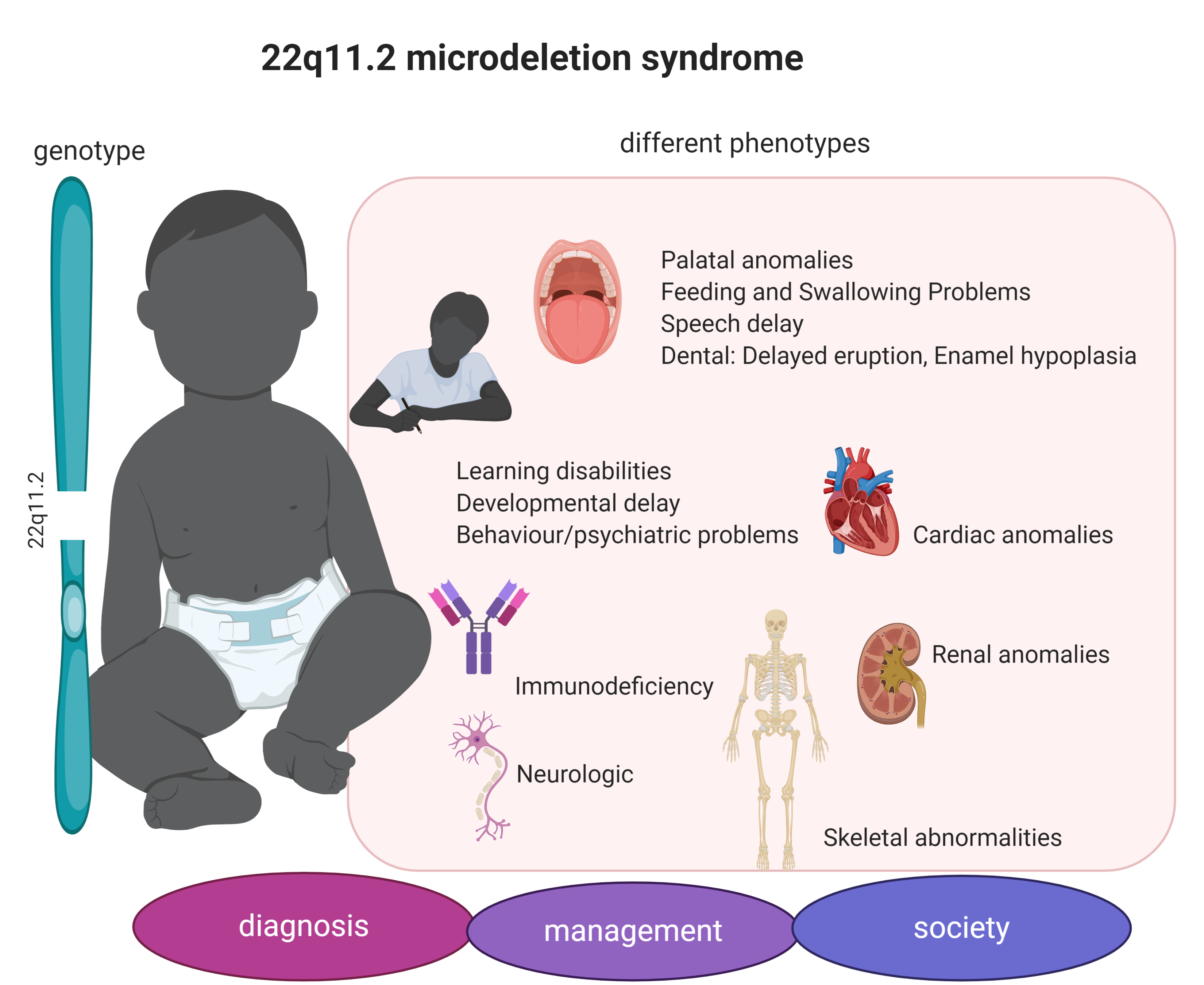
This can happen by chance when sperm and eggs are made. One of the most common structural chromosome abnormalities detected prenatally is a deletion of 22q1121 associated with DiGeorgeVelo-cardio-Facial VCF syndrome. Velocardiofacial syndrome VCFS and DiGeorge syndrome DGS are well-characterized syndromes with multisystem involvement dysmorphic facial features and cognitive disabilities.
2 4 In. Most of the diagnoses 868 were prompted by abnormal ultrasound findings heart defects HDs in 838 of cases. Often the infants have erythroderma similar to what is seen in Omenn syndrome.
In about 9 in 10 cases 90 the bit of DNA was missing from the egg or sperm that led to the pregnancy. The most common findings include 9 1. Prenatal detection by ultrasound is reported to be in 68 overall and sonographic findings are evident in 92 of those with complete monosomy X and 56 of those with mosaicism for monosomy X.
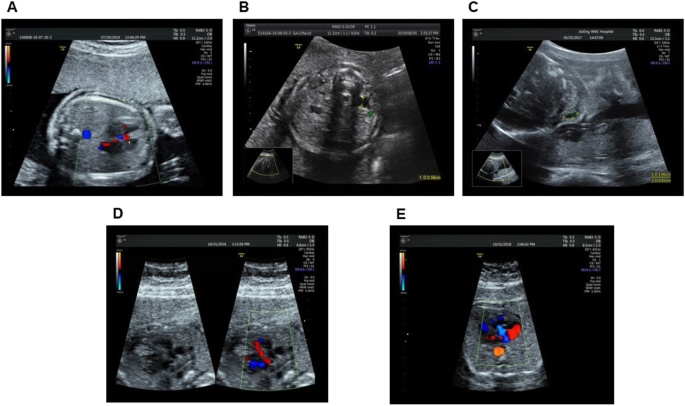
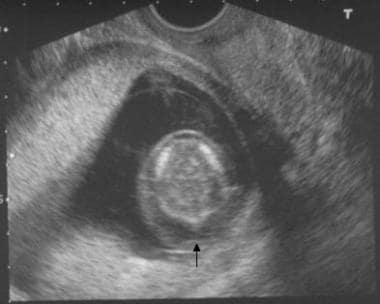
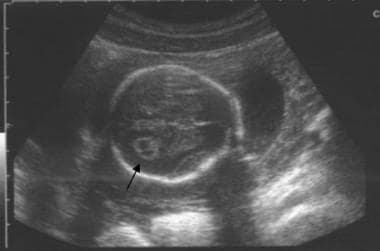
In some cases prenatal detection is in the later third-trimester because of the recognition of congenital cardiac anomalies. Historically this deletion has been identified using fluorescent in situ hybridization FISH with the TUPLE1 probe in fetuses presenting with a major heart defect detected by ultrasound. On fetal autopsy HDs were again the most common disease feature but thymus kidney abnormalities and facial dysmorphism were also described.
The ultrasound findings were used to modify the fetal risk for DiGeorge syndrome prior to counseling with amniocentesis for the purpose of molecular karyotyping by array comparative genomic hybridization CGH offered to all patients. 98 The T-cell counts are often quite high but do not reflect the adequacy of the T-cell compartment since they are expanded from a very small number of founder T cells. Parents were non-consanguineous with unremarkable family history.
DiGeorge syndrome is caused by a problem called 22q11 deletion. Some infants with thymic aplasia due to DiGeorge syndrome or chromosome 22q112 deletion syndrome have a dramatic oligoclonal expansion with infiltration into end organs.
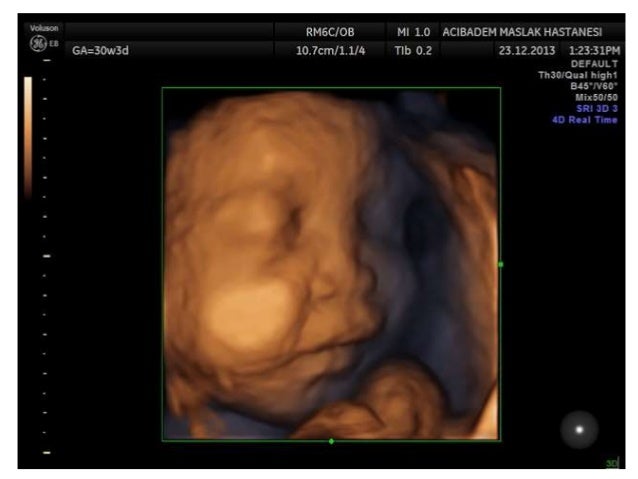
This article provides an overview of the prenatal sonographic features of del22q112 syndrome including cardiovascular abnormalities thymic hypoplasia or aplasia intrauterine growth restriction urinary abnormalities increased nuchal translucency thickness and abnormal.
Prenatal detection by ultrasound is reported to be in 68 overall and sonographic findings are evident in 92 of those with complete monosomy X and 56 of those with mosaicism for monosomy X. Velocardiofacial syndrome VCFS and DiGeorge syndrome DGS are well-characterized syndromes with multisystem involvement dysmorphic facial features and cognitive disabilities. This can happen by chance when sperm and eggs are made. One of the most common structural chromosome abnormalities detected prenatally is a deletion of 22q1121 associated with DiGeorgeVelo-cardio-Facial VCF syndrome. 2 4 In. Current indications for prenatal testing for the 2q112 deletion include 1 a previous child with a 22q112 deletion or DiGeorgevelocardiofacial syndrome 2 an affected parent with a 22q112. In some cases prenatal detection is in the later third-trimester because of the recognition of congenital cardiac anomalies. A 35-year-old healthy primigravida was hospitalized due to preterm labor at 29 weeks and four days. Heart anomalies 80 of patients Frequent infections due to immunodeficiencyT-cell deficiency Developmental delay including speech delay learning disabilities and delayed growth Hypocalcemia which can lead to seizures beginning in the neonatal period.
Parents were non-consanguineous with unremarkable family history. Figure 1 Open in figure viewer PowerPoint. Mosaic Turner syndrome signifies that the abnormalities only occur in the X chromosome of some of the cells in the body2 Turner syndrome is usually not inherited because it occurs during a random event during the for-mation of reproductive cells in the affected persons parents12 Classic sonographic findings of Turner syndrome. 1 It is typically caused by a sporadic uneven recombination event resulting in hemizygous deletion of approximately 3 megabases on the long arm of chromosome 22. One of the most common structural chromosome abnormalities detected prenatally is a deletion of 22q1121 associated with DiGeorgeVelo-cardio-Facial VCF syndrome. This article provides an overview of the prenatal sonographic features of del22q112 syndrome including cardiovascular abnormalities thymic hypoplasia or aplasia intrauterine growth restriction urinary abnormalities increased nuchal translucency thickness and abnormal. A 35-year-old healthy primigravida was hospitalized due to preterm labor at 29 weeks and four days.



































Post a Comment for "Digeorge Syndrome Ultrasound Findings"