Damper In Mechanical System
Damper in mechanical system. Examples include viscous drag a liquids viscosity can hinder an oscillatory system causing it to slow down in mechanical systems resistance in electronic oscillators and absorption. All the materials exhibit the Translational property of damping to iii Damper some extent. Note that the system above has no input it is unforced.
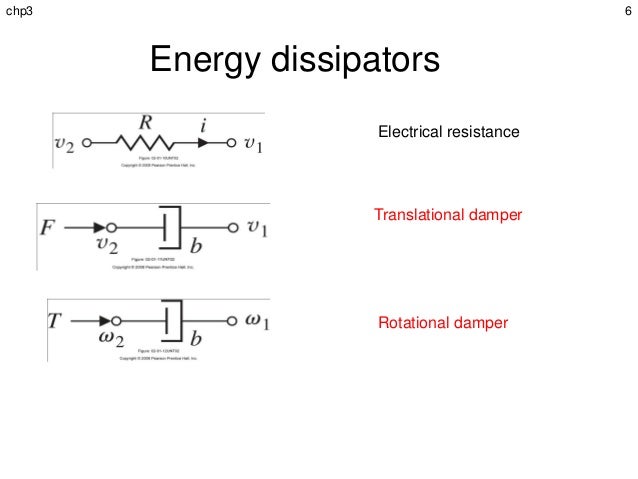
Similarly there is a torque current analogy for rotational mechanical systems. In this analogy the mathematical equations of the rotational mechanical system are compared with the nodal mesh equations of the electrical system. Spring mass damper system is a very common scenario that is taught in mechanical engineering.
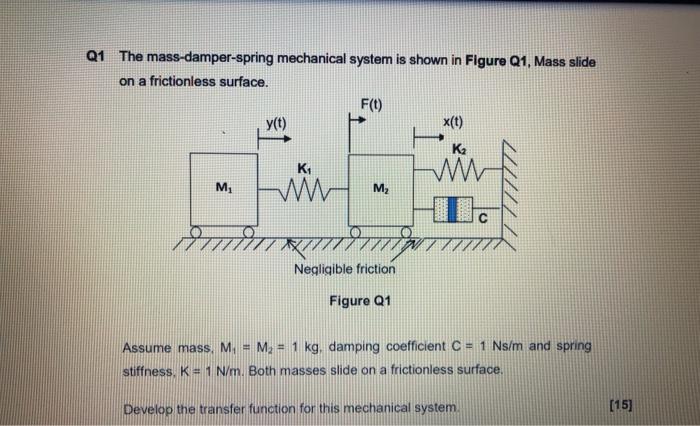
Dampers Connections Dampers in series. Those are mass spring and dashpot or damper. To be an energy-dissipating effect a device must exert a force opposite to the velocity.
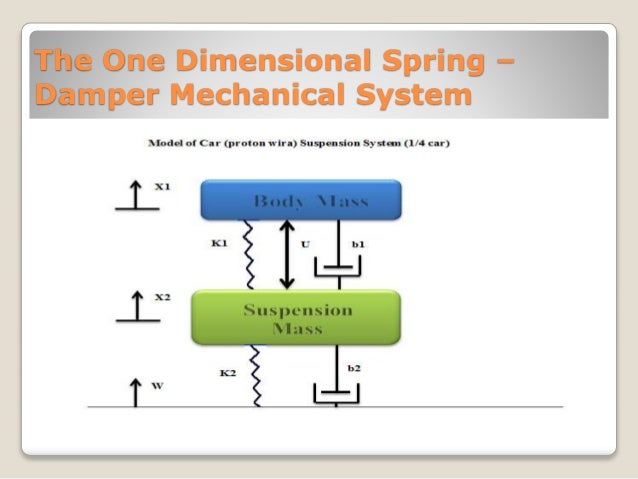
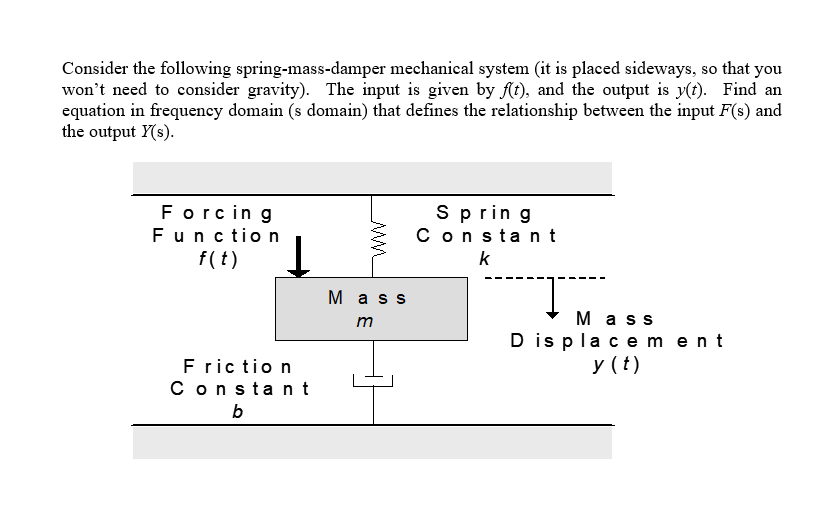
Practical examples of this system are mostly seen in the suspension of a vehicle. If a force is applied to a translational mechanical system then it is opposed by opposing forces due to. F M x Translational Damper When the viscosity or drag is not negligible in a system we often model them with the damping force.
A damper is an element that provides resistance in mechanical motion and as such its effect on the dynamic behavior of a mechanical system is similar to that of an electrical resistor on the dynamic behavior of an electrical system. Damping is an influence within or upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing or preventing its oscillation. In physical systems damping is produced by processes that dissipate the energy stored in the oscillation.
A damper may be used to cut off central air conditioning heating or cooling to an unused room or to regulate it for room-by. Dampers - commonly called shock absorbers - perform this function. What are mechanical dampers in 40 secondssorry for the spelling mistake httpopencoursewarekfupmedusacollegescesmeme413files5C2-Chapters_CHAPT.
He also proposed an inerter design that has an insignificant mass compared to the energy it is capable of storing. While the previous page System Elements introduced the fundamental elements of translating mechanical systems as well as their mathematical models no actual systems were discussed.
Nothing forces the system to.
Opening the damper enables air from outside a building to go into in order to cool the interior or it can close to consist of the within air. Let us now discuss this analogy. Note that the system above has no input it is unforced. By comparing Equation 4 and Equation 6 we will get the analogous quantities of rotational mechanical system. Damper flow a mechanical device in a duct or chimney that regulates airflow. Similarly there is a torque current analogy for rotational mechanical systems. Practical examples of this system are mostly seen in the suspension of a vehicle. Translational mechanical systems move along a straight line. In Shortto reduce the vibration damper is used in mechanical system.
Similarly there is a torque current analogy for rotational mechanical systems. Spring mass damper system is a very common scenario that is taught in mechanical engineering. To be an energy-dissipating effect a device must exert a force opposite to the velocity. Those are mass spring and dashpot or damper. Similarly there is a torque current analogy for rotational mechanical systems. If a force is applied to a translational mechanical system then it is opposed by opposing forces due to. Damping is an influence within or upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing or preventing its oscillation.





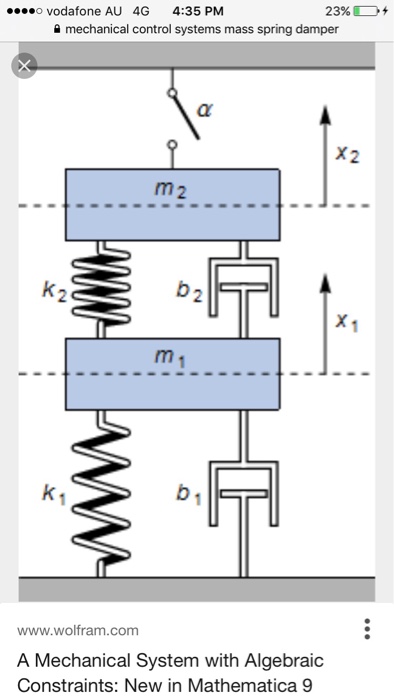




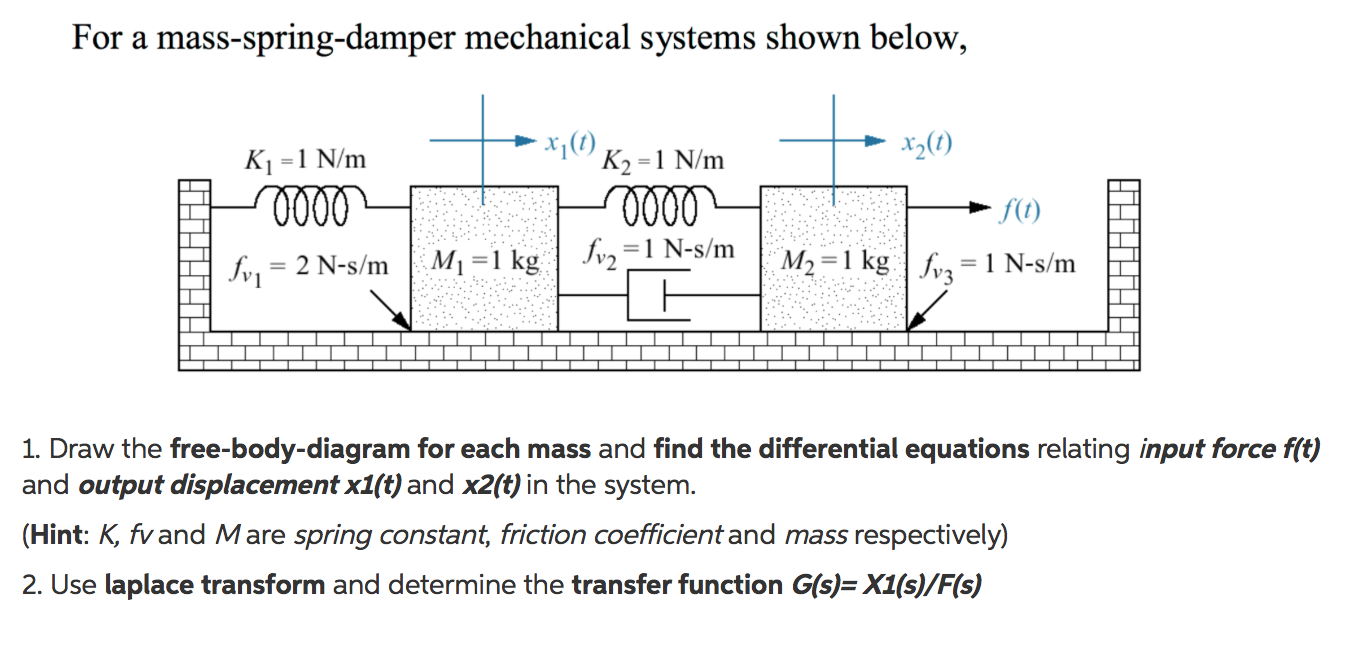



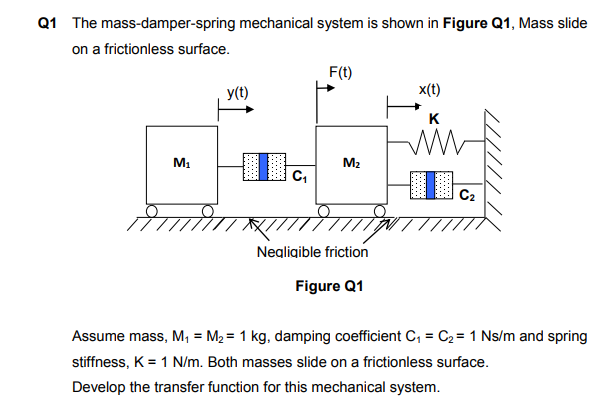



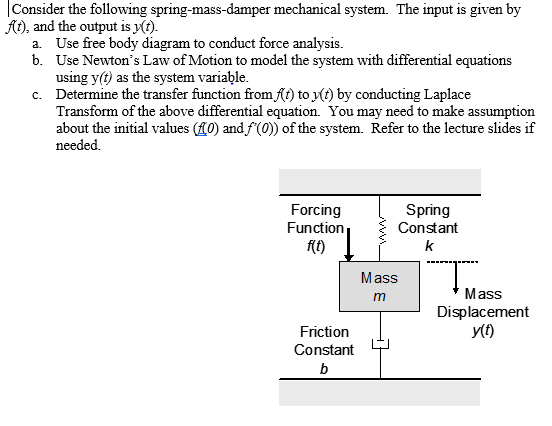



















Post a Comment for "Damper In Mechanical System"