Pathology Of Coronary Heart Disease
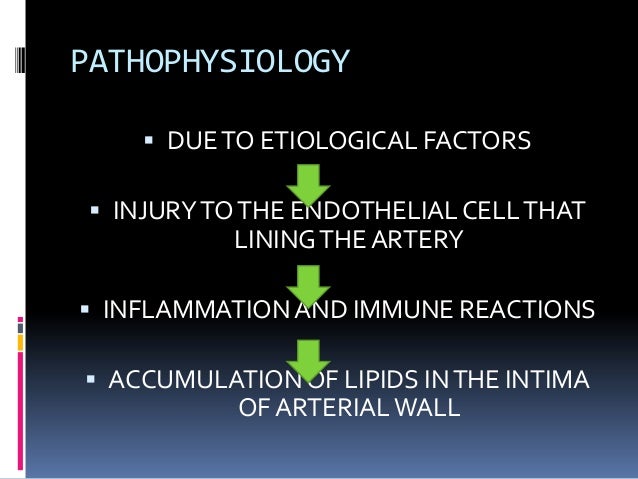
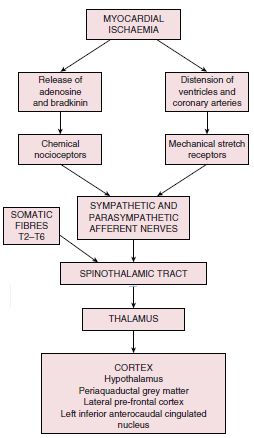
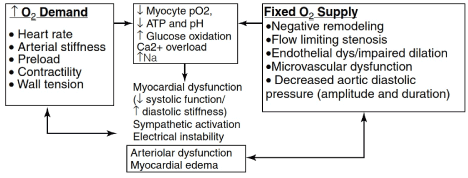
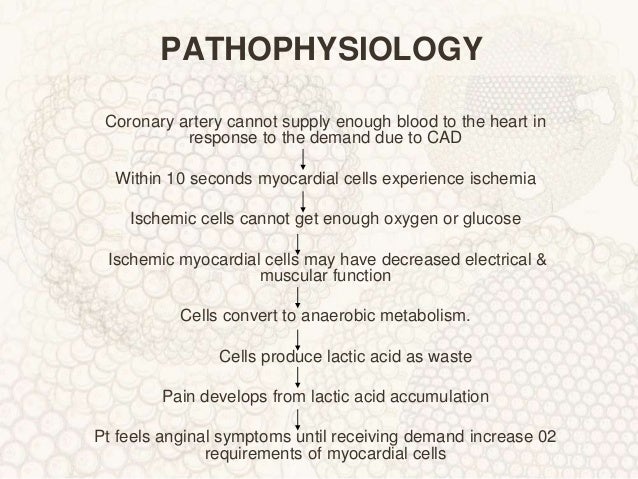
Pathology of coronary heart disease. Stable coronary artery disease CAD or SIHD refers to the syndrome of recurrent transient episodes of chest pain reflecting demand-supply mismatch that is angina pectoris. 2952575 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE Publication Types. Reduced oxygen supply to the heart is defined myocardial ischemia which results in a severely reduced ability of the heart muscle ability to contract.
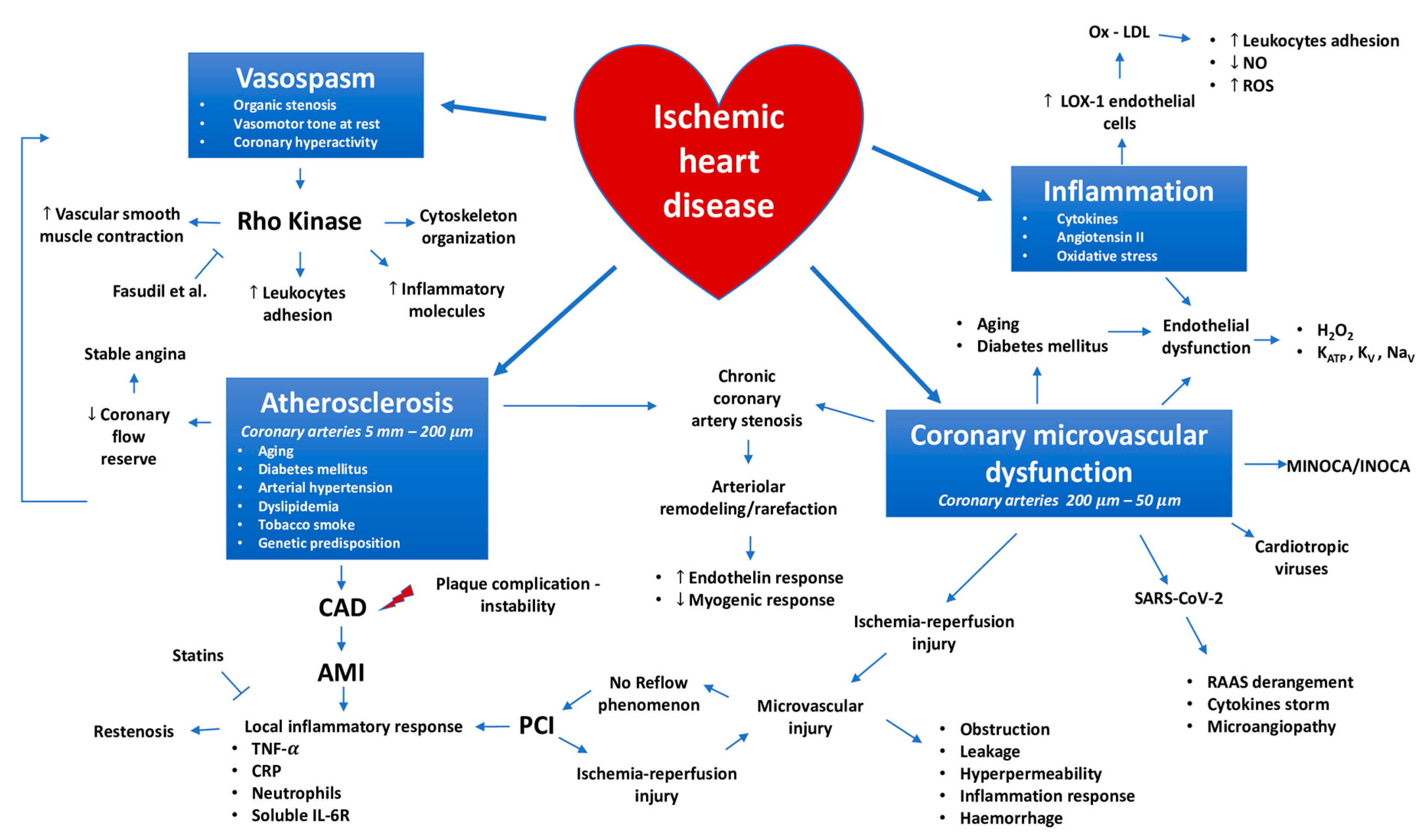
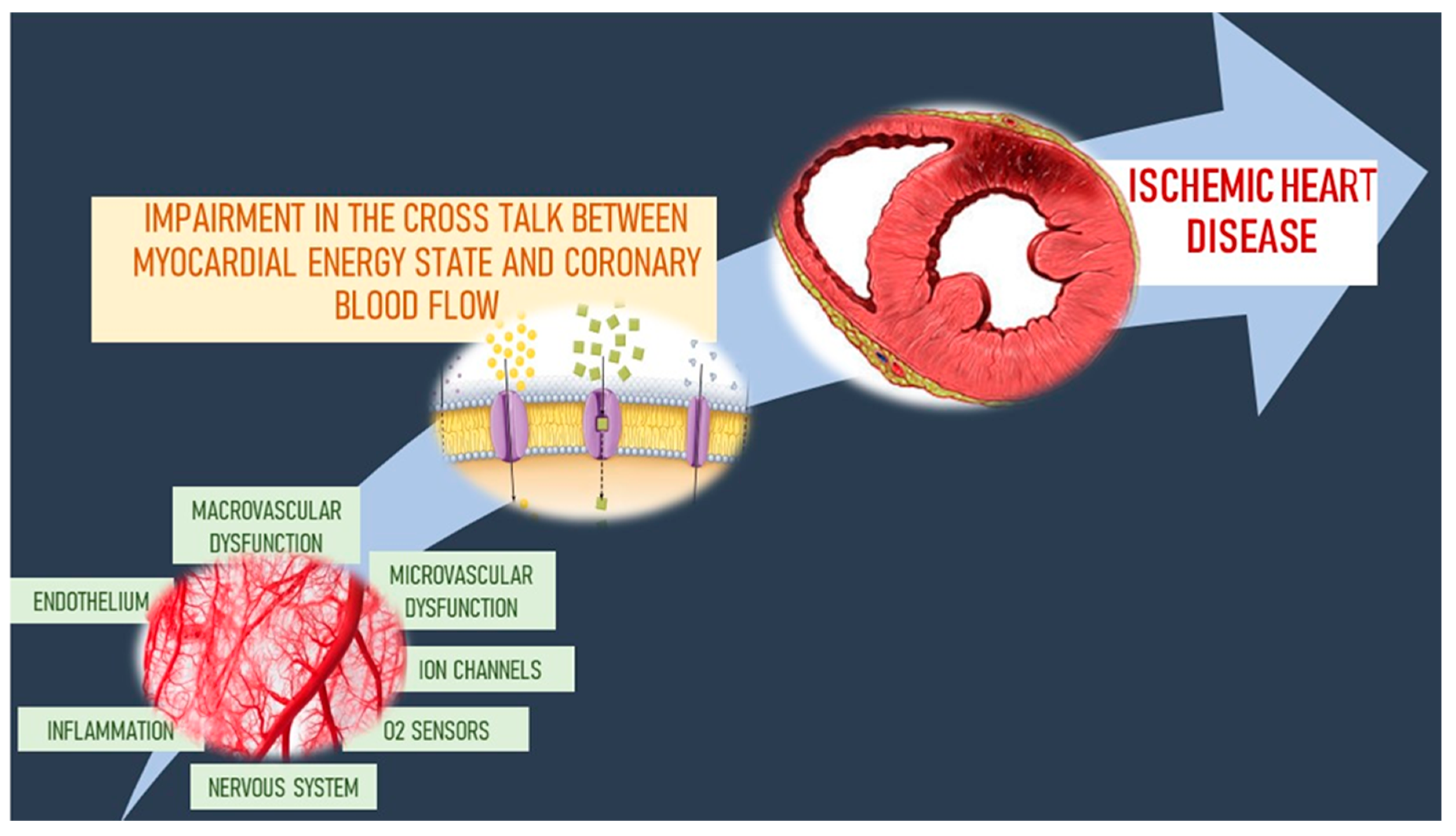
The clinical presentations of coronary artery disease are diverse and not clearly linked to the severity or extent of the disease. Coronary Disease pathology. During the past decade our understanding of the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease CAD has undergone a remarkable evolution.
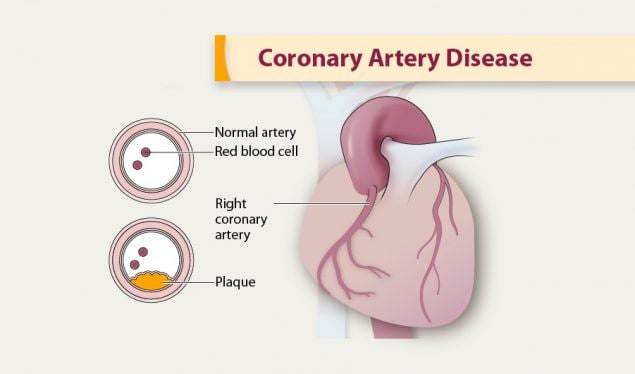
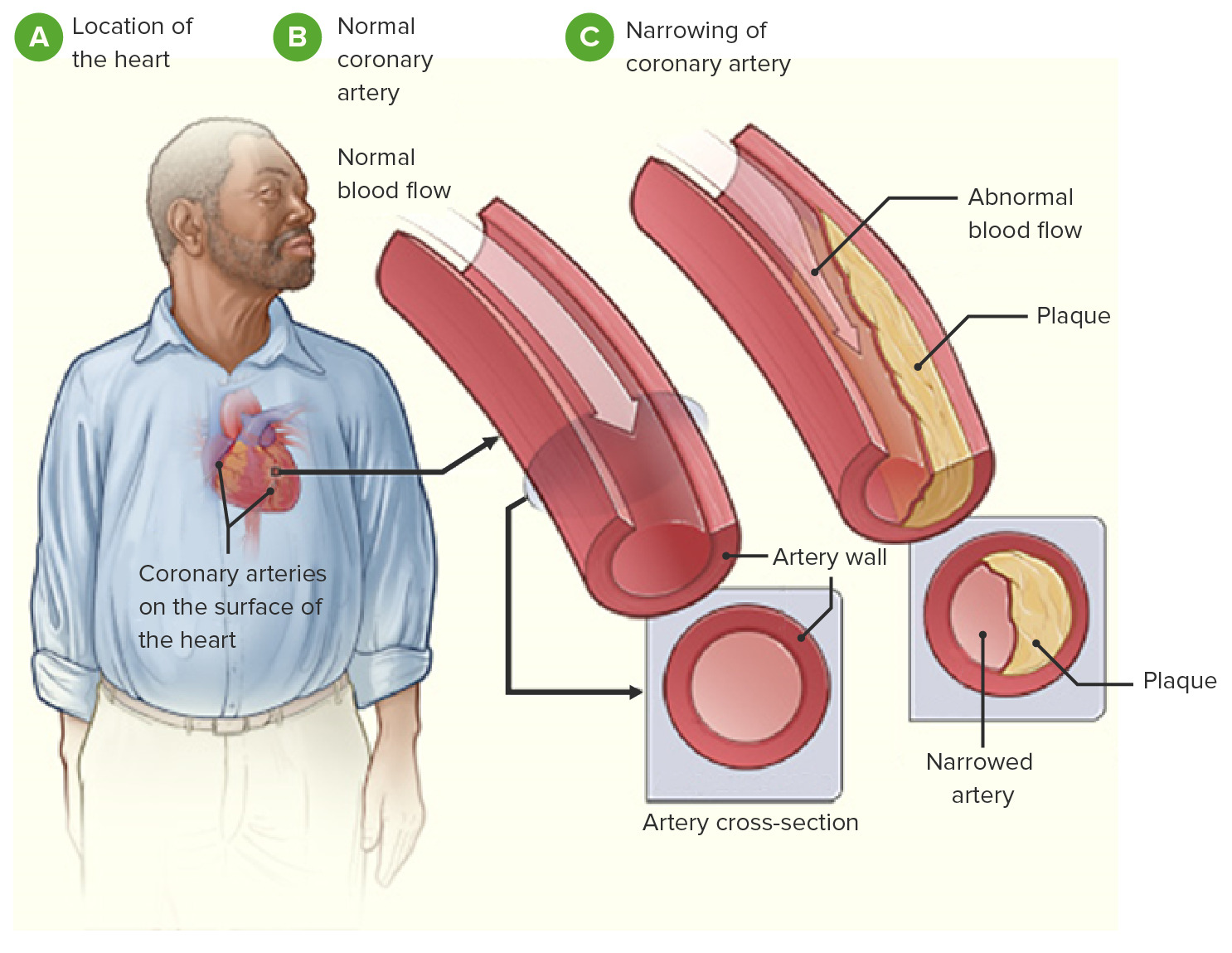
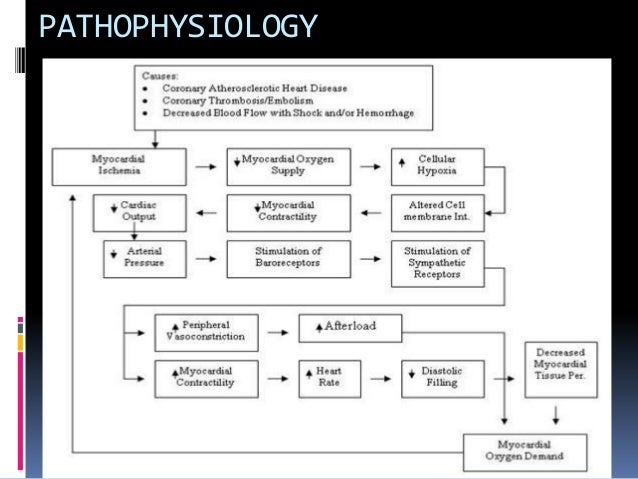
All three have coronary artery disease which is defined as an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply from the coronary arteries. Coronary heart disease disease characterized by an inadequate supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle myocardium because of narrowing or blocking of a coronary artery by fatty plaques see atherosclerosis. The distribution of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with ischemic heart disease is extensive and involves at least two major coronary arteries.
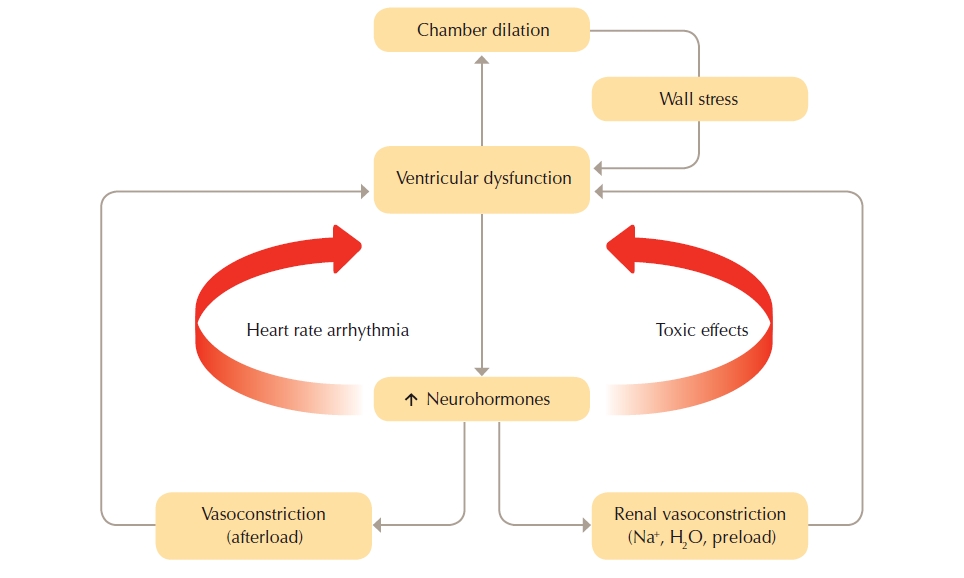
Coronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology. In affluent societies coronary artery disease causes severe disability and more death than any other disease including cancer. However many patients die suddenly due to arrhythmia a long time before the loss of myocardium disturbs left ventricular pump function so severely that lethal heart failure may develop.
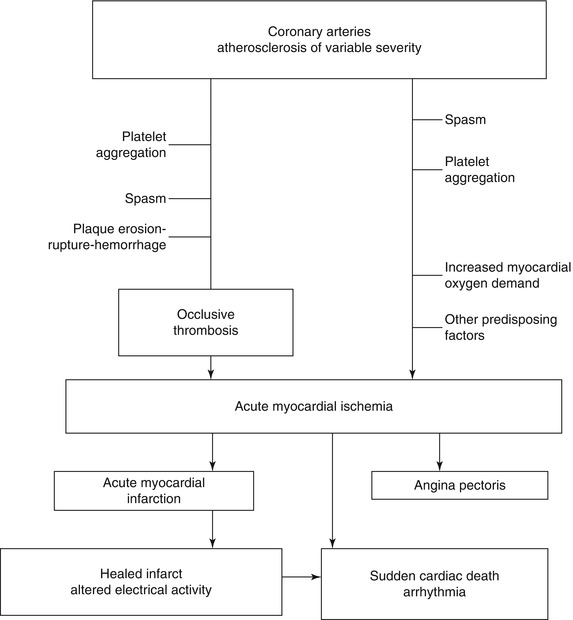
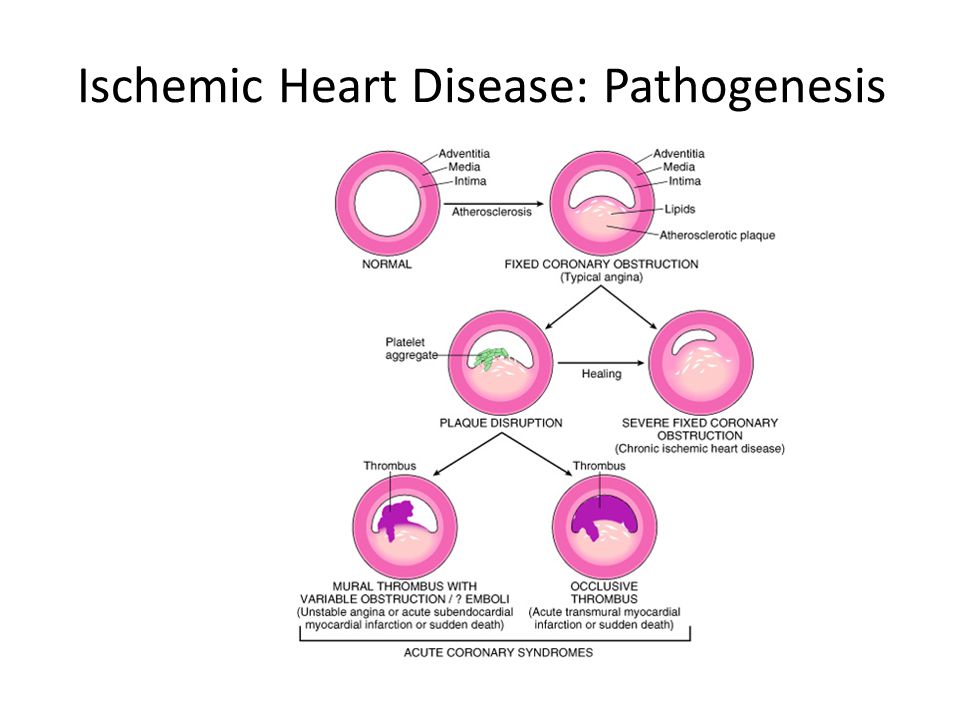
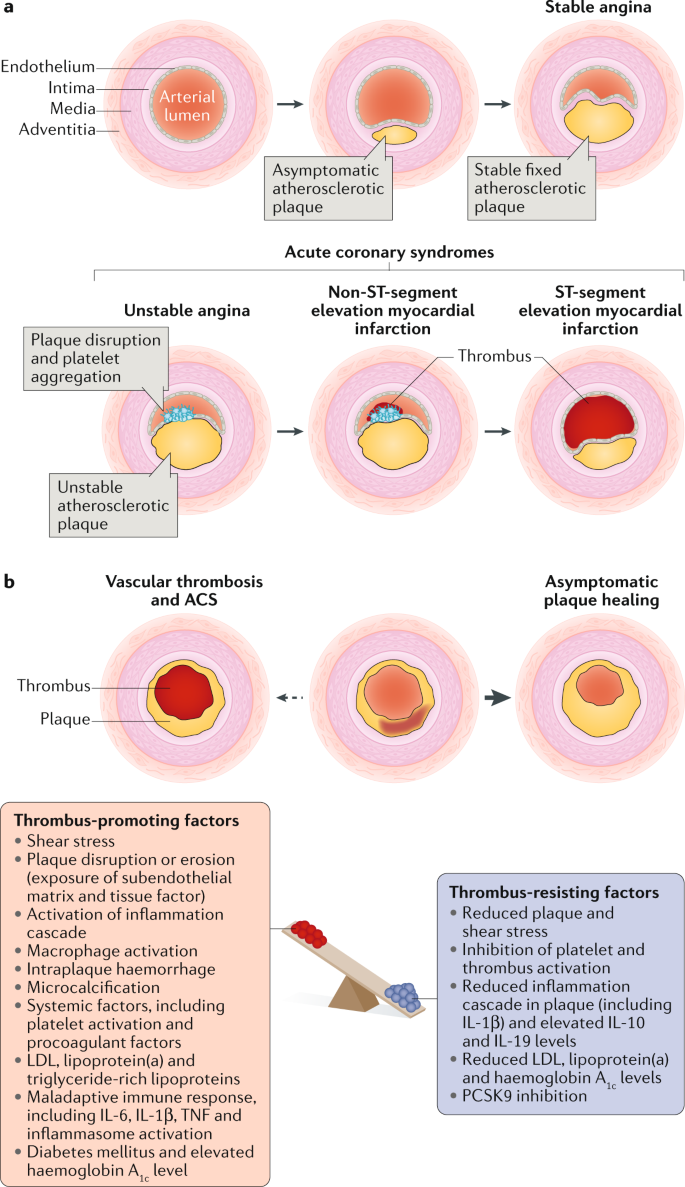
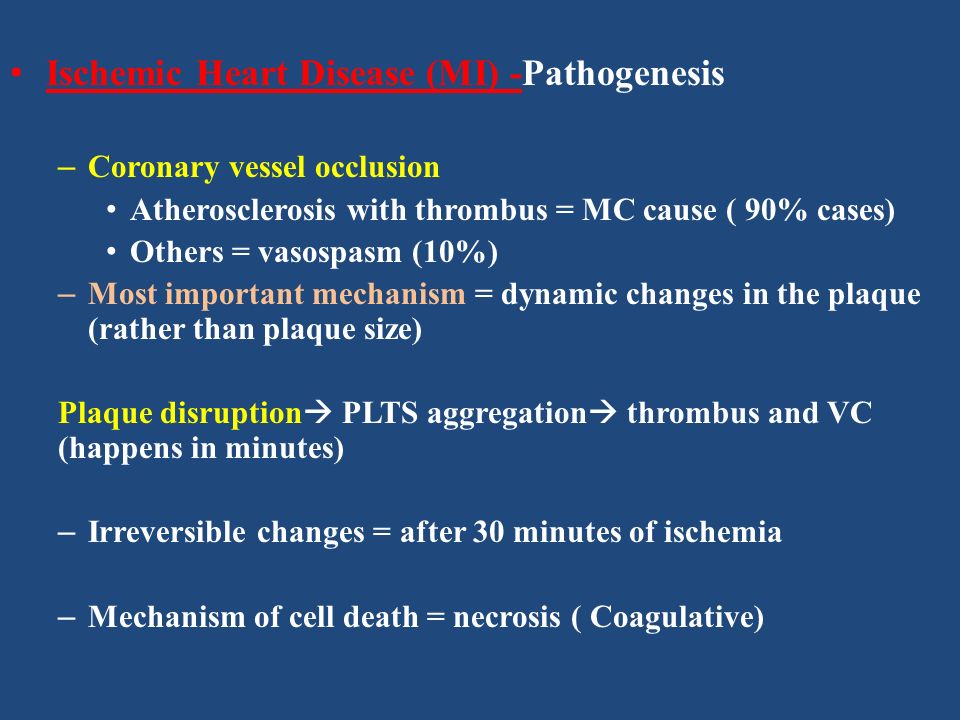
Coronary arteritis is discussed chiefly in the context of Kawasaki disease but polyarteritis and eosinophilic arteritis are also described. Clinical and Pathological Aspects of Heart Disease The vast majority of myocardial infarcts result from complications of coronary atherosclerosis. Necropsy studies suggest that a new thrombotic coronary event underlies 5070 of sudden deaths caused by ischaemic heart disease.
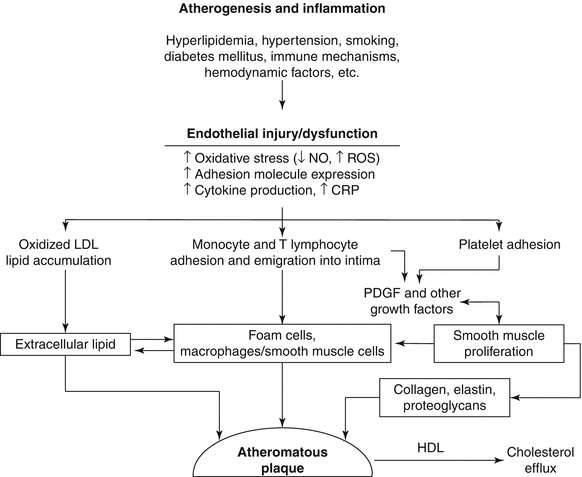
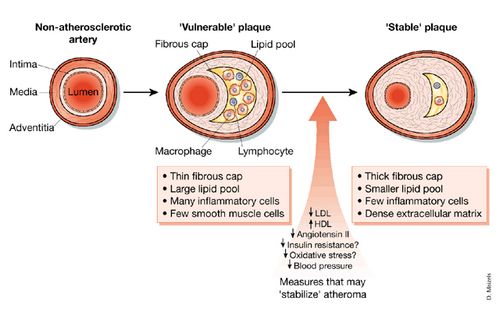
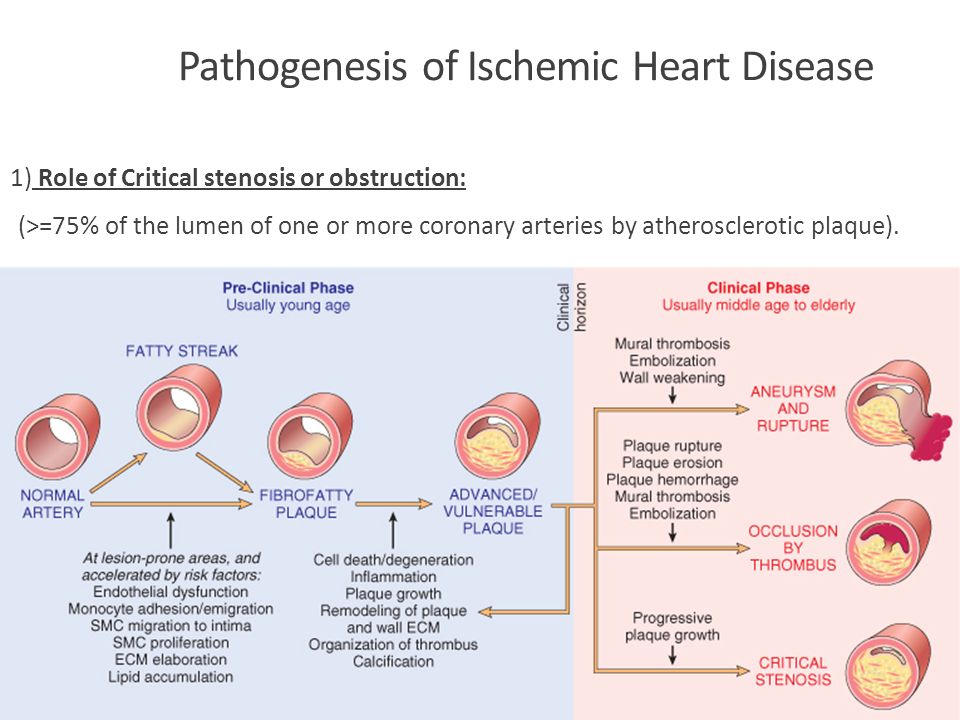
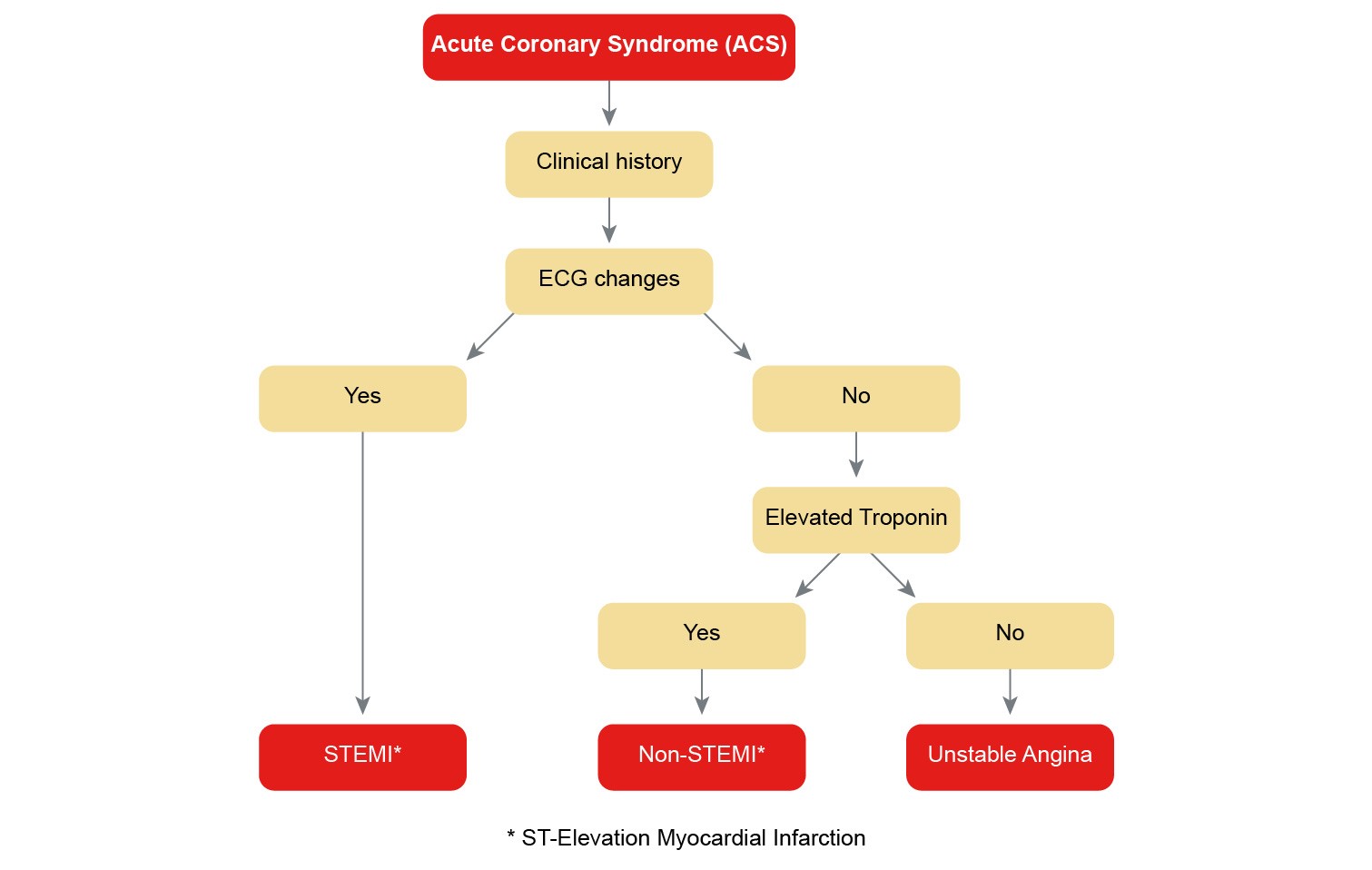
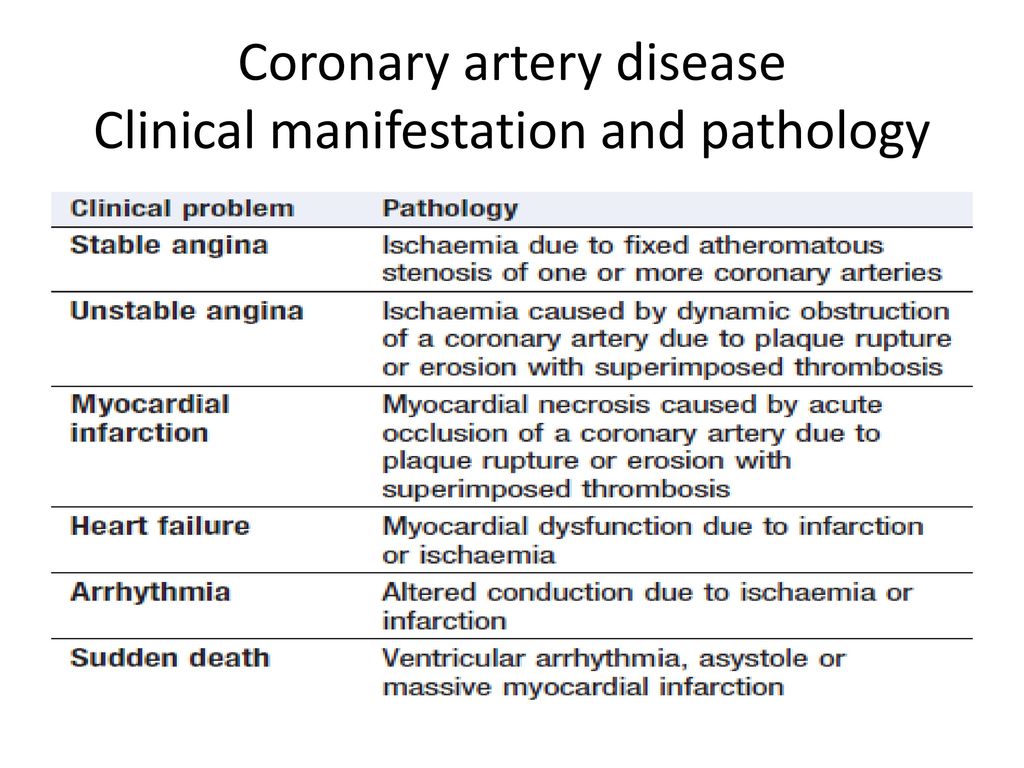
Coronary artery disease is usually caused by a build up cholesterol rich deposits or plaques on the lining inside the artery. It manifests as angina silent ischaemia unstable angina myocardial infarction arrhythmias heart failure and sudden death. Pathology of Coronary Heart Disease.
Given the importance of thrombosis as the trigger for acute myocardial ischaemia it is necessary to know something about the structure of plaques before thrombotic events occur and why there should be a sudden. Coronary Disease mortality.
We focus on disorders of coronary artery function and their.
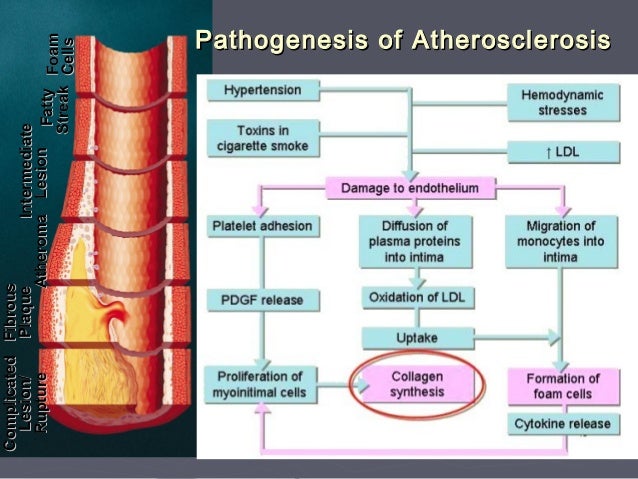
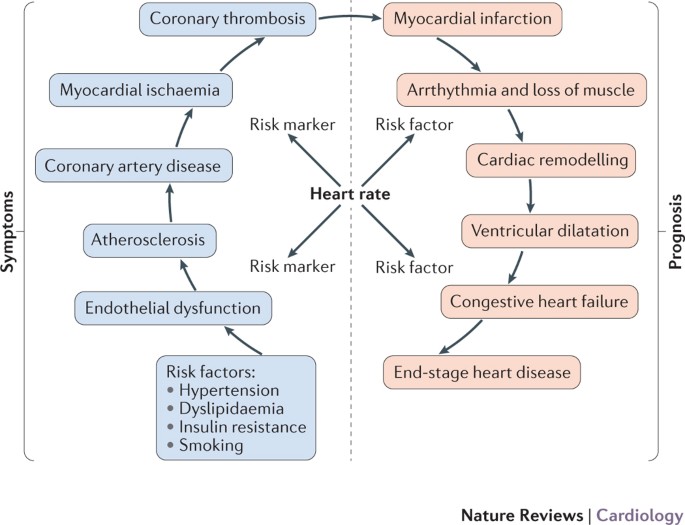
In affluent societies coronary artery disease causes severe disability and more death than any other disease including cancer. Coronary artery disease occurs when there is a narrowing of the coronary arteries due to the development of plaques leading to reduce amounts of oxygenated blood to the heart. Coronary Artery Disease diagnosis. Coronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology. Plaque is made up of cholesterol deposits. The distribution of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with ischemic heart disease is extensive and involves at least two major coronary arteries. All three have coronary artery disease which is defined as an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply from the coronary arteries. Coronary Disease pathology. Stable coronary artery disease CAD or SIHD refers to the syndrome of recurrent transient episodes of chest pain reflecting demand-supply mismatch that is angina pectoris.
The distribution of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with ischemic heart disease is extensive and involves at least two major coronary arteries. Coronary artery disease is usually caused by a build up cholesterol rich deposits or plaques on the lining inside the artery. In this article we reappraise the causes of angina based on new insights into coronary pathophysiology. Coronary artery disease occurs when there is a narrowing of the coronary arteries due to the development of plaques leading to reduce amounts of oxygenated blood to the heart. Coronary heart disease disease characterized by an inadequate supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle myocardium because of narrowing or blocking of a coronary artery by fatty plaques see atherosclerosis. Fibromuscular dysplasia is treated in some detail and idiopathic arterial calcification rounds off the chapter. Pathology of Coronary Heart Disease.























Post a Comment for "Pathology Of Coronary Heart Disease"